Basic Usage
In a Modern.js application, developers can define API files under the api/lambda directory and export API functions from these files. In the frontend code, these API functions can be directly invoked by importing the file, which initiates the API requests.
This invocation method is called unified invocation, where developers do not need to write glue code for the frontend and backend separately, thereby ensuring type safety across both.
Enable BFF
To enable BFF functionality in a Modern.js project, follow these steps to modify the code:
- Install BFF plugin dependencies
If the BFF plugin is not yet installed in your project, install it first:
Make sure the version of @modern-js/plugin-bff matches the version of @modern-js/app-tools in your project. All Modern.js official packages are released with a uniform version number, and version mismatches may cause compatibility issues.
Check the version of @modern-js/app-tools first, then install the same version of @modern-js/plugin-bff:
- Configure
modern.config.ts
Import and add the BFF plugin in the modern.config.ts file:
- Configure TypeScript alias
To correctly recognize the @api alias in TypeScript, it is recommended to add path mapping in tsconfig.json:
BFF Functions
Functions that allow unified invocation are called BFF Functions. Here is an example of the simplest BFF function. First, create the api/lambda/hello.ts file:
Then, import and invoke the function directly in src/routes/page.tsx:
The function imported in src/routes/page.tsx will be automatically converted into an API call, eliminating the need to use an SDK or Web Fetch to call the API.
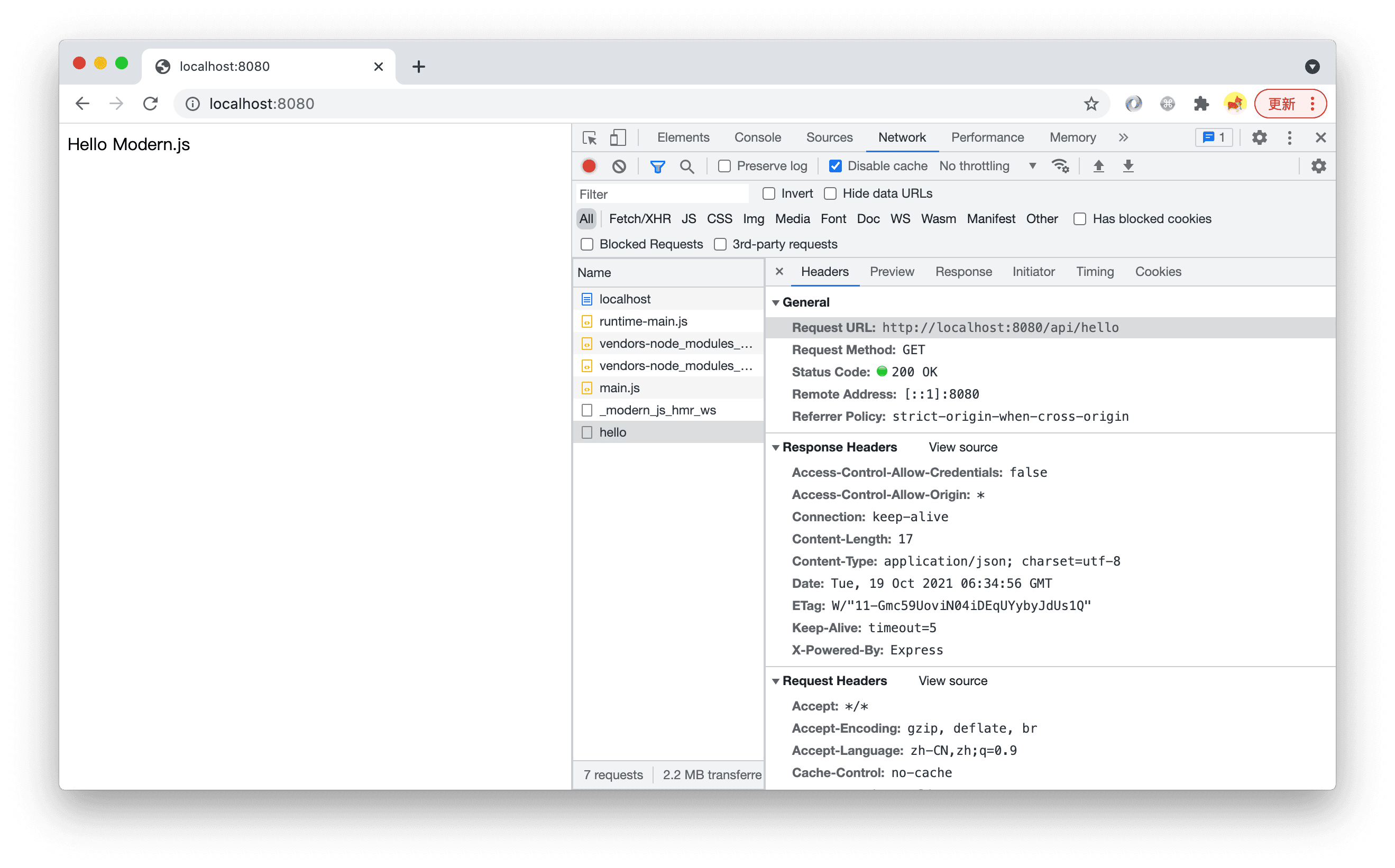
After running pnpm run dev, open http://localhost:8080/ and you can see that the page displays the content returned by the BFF function. In the Network tab, you can see a request was made to http://localhost:8080/api/hello.
Function Routes
In Modern.js, the routing system for BFF functions is implemented based on the file system, which is another form of conventional routing. Each BFF function in the api/lambda directory is mapped to an API route. Here are some routing conventions.
All routes generated by BFF functions have a common prefix, which defaults to /api. This can be configured using bff.prefix.
Default Routes
Files named index.ts will be mapped to the parent directory.
api/lambda/index.ts->{prefix}/api/lambda/user/index.ts->{prefix}/user
Nested Routes
Nested directories are supported, and files will be automatically parsed into routes in the same way.
api/lambda/hello.ts->{prefix}/helloapi/lambda/user/list.ts->{prefix}/user/list
Dynamic Routes
Similarly, creating a directory or file with [xxx] in the name supports dynamic route parameters. The rules for dynamic route function parameters can be found in dynamic-path.
api/lambda/user/[username]/info.ts->{prefix}/user/:username/infoapi/lambda/user/username/[action].ts->{prefix}/user/username/:action
Whitelist
By default, all files under the api/lambda/ directory are parsed as BFF function files, but the following files are ignored:
- Files starting with an underscore
_. For example:_utils.ts. - Files under directories starting with an underscore
_. For example:_utils/index.ts,_utils/cp.ts. - Test files. For example:
foo.test.ts. - TypeScript type files. For example:
hello.d.ts. - Files under
node_modules.
RESTful API
Modern.js BFF functions need to follow RESTful API standards for definition. Developers must define BFF functions according to a set of rules.
BFF functions should not only be invoked within the project but also be accessible to other projects via an SDK or Web fetch. Therefore, Modern.js does not define a private protocol for unified invocation but uses standard HTTP methods along with common HTTP request parameters like params, query, and body to define functions.
Function Export Rules
HTTP Method Named Functions
Modern.js BFF functions' export names determine the HTTP method for the corresponding API, such as get, post, etc. For example, to export a GET API:
The following example exports a POST API:
-
Modern.js supports 9 HTTP methods:
GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,CONNECT,TRACE,PATCH,OPTIONS, andHEAD, which can be used as function export names. -
Names are case-insensitive. If the method is
GET, it can be written asget,Get,GEt, orGET, and the default export, i.e.,export default xxx, will be mapped toGet.
Using Async Functions
Modern.js recommends defining BFF functions as async functions, even if there is no asynchronous process in the function, for example:
This is because, during frontend invocation, the BFF function will be automatically converted into an HTTP API call, and HTTP API calls are asynchronous. On the frontend, it is typically used like this:
Therefore, to keep the type definitions consistent with the actual invocation experience, we recommend defining BFF functions as async functions.
Function Parameter Rules
Function parameter rules are divided into two parts: dynamic routes in the request path (Dynamic Path) and request options (RequestOption).
Dynamic Path
Dynamic routes will be the first part of the BFF function parameters, with each parameter corresponding to a segment of the dynamic route. For example, the level and id parameters will be passed to the function in the following example:
Invoke the function by directly passing in the dynamic parameters:
RequestOption
Parameters following the dynamic path are an object called RequestOption, which includes the query string and request body. This field is used to define the types for data and query.
In a standard function without dynamic routes, RequestOption can be obtained from the first parameter, for example:
Custom types can also be used here:
When the function file uses dynamic routing, dynamic routes will precede the RequestOption object parameter.
Pass the corresponding parameters when invoking the function according to its definition:
Extend BFF Function
The standard BFF function writing method may not always meet your needs. For example, complex TS type requirements in business scenarios. Modern.js provides a more powerful BFF function writing method.
For more details, please refer to - Creating Extensible BFF Functions.
Code Sharing
Besides the BFF functions in the api/ directory, which can be referenced in the src/ directory through an integrated calling method, the src/ and api/ directories cannot directly reference each other's code by default. To achieve code sharing, a shared directory can be created at the root of the project for both src/ and api/ to use commonly.
